Historians study various subjects, including politics, diplomacy, economics, and social customs. However, they are chiefly concerned with uncovering their chosen topic’s historical context.
Historical understanding requires people to take multiple perspectives on a topic. This strategy promotes essential skills in historical thinking.
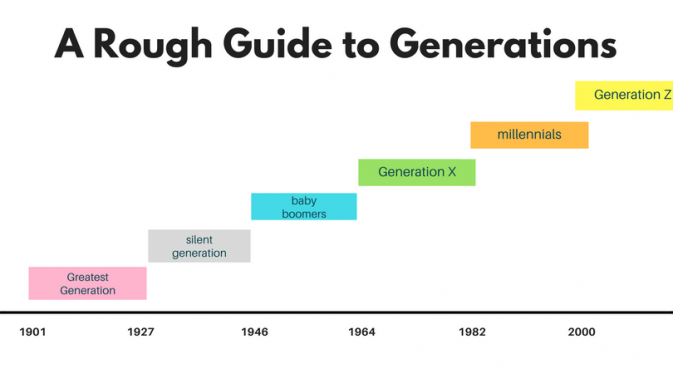
How Many Years in a Generation Has Changed Over Time?
Generational cohorts have long interested demographers, social scientists, and researchers. Generational names like Millennials, Gen Xers, baby boomers, and Silent Generation are often used in research papers and media stories to compare generations. When evaluating generational trends, it is essential to understand the difference between family generations and social generations. Family generations are the biologically-based groupings of people that are typically based on birth dates. Social generations are broader in scope and are defined by the events, experiences, political climate, and beliefs that shape people’s lives.
A critical factor in defining a generation is the political climate that is experienced at an early age. This can include the presidents that a generation reached adulthood during, the economic and social conditions of their time, and the overall political climate of their country.
For example, Millennials grew up during the rise of social media, mobile phones, and a technologically driven world. They have a different outlook on life than the generations before them and are likelier to value learning through experience over education.
This makes it easy to see why they have a different views on things such as the environment, equality, and violence. They also strongly believe in the need for work/life balance and don’t hold jobs for life as the boomers did.
What is a Generation?
It’s essential to understand what is a generation and its brief importance. A generation is a group of people that share everyday experiences and attitudes. These experiences can include how they view the world, their attitudes toward work and family, and their values and beliefs. Traditionally, generations are defined by age and birth years. These groups are often referred to by their popular generation names, such as GI Generation, Silent Generation, Baby Boomers, Generation X, Millennials, and Gen Z.
These groups are shaped by the history of their time and the era they grew up in. This can significantly impact their attitudes, values, and behaviors. For example, the GI Generation was influenced by the crisis era of World War II and the Great Depression. This led to their resentment of authority and the need for security. On the other hand, the Millennials were raised in an era of values experimentation and youth rebellion. This caused them to question the status quo and seek new life opportunities.
The word generation comes from Latin, meaning a step in natural descent. It also describes a class or type of object: a third-generation car or a new generation of anticancer drugs. In modern usage, a generation is a group of people that share the same experience at a particular point in history and have similar attitudes, values, and interests.
What is a Historical Perspective?
Historical perspective is the ‘point of view’ from which the creator of a source describes historical events. People see the world differently based on age, gender, social position, and beliefs. This is why it’s essential to identify the perspective of a source when researching any historical topic. This will help you understand WHY the author has a particular opinion about a specific event. For example, if an academic historian writes that the English Civil War was a power struggle between different social classes, you will know that their political views influenced their perspective.
It’s also essential to consider other people’s perspectives when interpreting history. For example, two opposing fans at a football match will have different views on the game. One may be happy with the result and discuss how great their team played. The other might be angry and blame the referees or the opposing team for cheating. This shows that personal opinions and biases continually shape perspectives.
Historical context is the set of circumstances that surrounds an occurrence’. It can include physical settings, religious or cultural beliefs, and societal customs. The study of history is most concerned with understanding how these factors have shaped the world at a particular time. With this understanding, it is possible to know why a decision was made and whether it was irrational.
What is the Historical Context?
Historical context is the social, economic, and cultural influences that shape a period. It can include a country’s major events, religious conditions, and cultural traditions and beliefs. Historical context also consists of a place’s political landscape and economic structure.
When you’re writing about history, it’s essential to understand the historical context of your topic. This will help you understand why something happened and how it influenced other events. It will also help you make informed judgments about a topic.
For example, if you’re researching the Stolen Generations in Australia, it would be essential to know that the country’s Indigenous peoples were treated as equal citizens in recent years. This could explain why the attitudes of those times were different from ours.
Similarly, if you’re analyzing the use of satire in Gulliver’s Travels, it’s essential to know that Whig politics were popular at the time. This will give you insight into how the humor was intended and why it might have succeeded.
When identifying the historical context of a text, it’s often necessary to do some sleuthing. This may involve reading the text carefully to identify keywords or hints about its period, or it may mean searching for background information on the author and the historical conditions at the time.